Intrinsic And Extrinsic Motivation Definition Psychology

It s the love of the game.
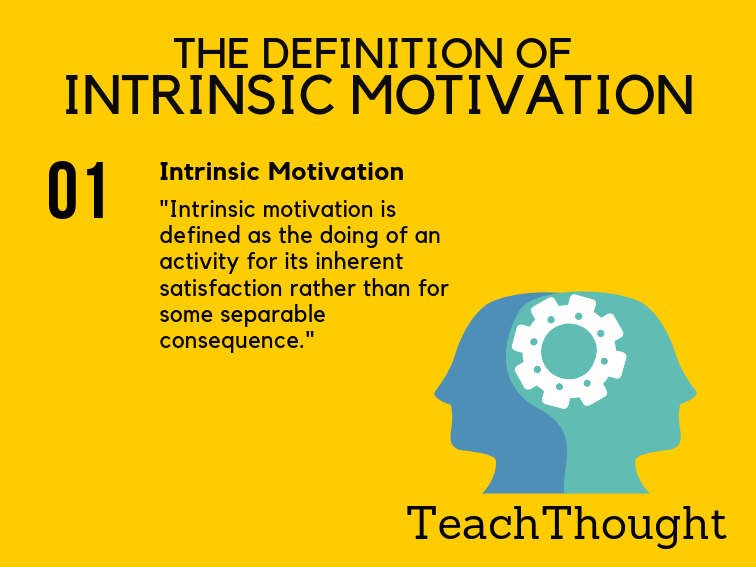
Intrinsic and extrinsic motivation definition psychology. It s intrinsic to the task. The act of being motivated by internal factors to perform certain actions and behavior is called intrinsic motivation. This type of motivation arises from outside the individual as opposed to intrinsic motivation which originates inside of the individual. Motivation drives us to get out of bed every day to accomplish something important to us.
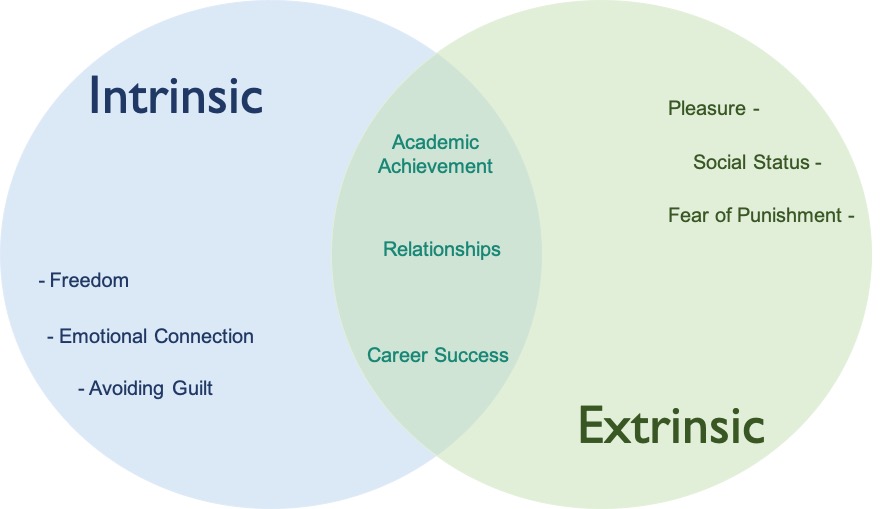
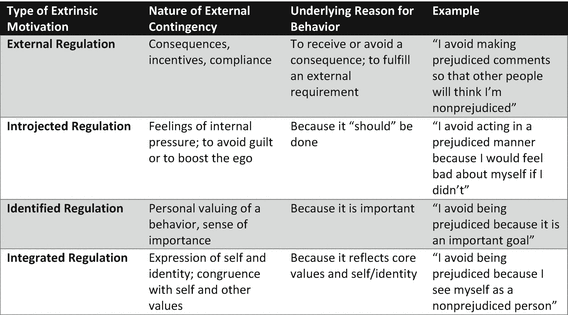
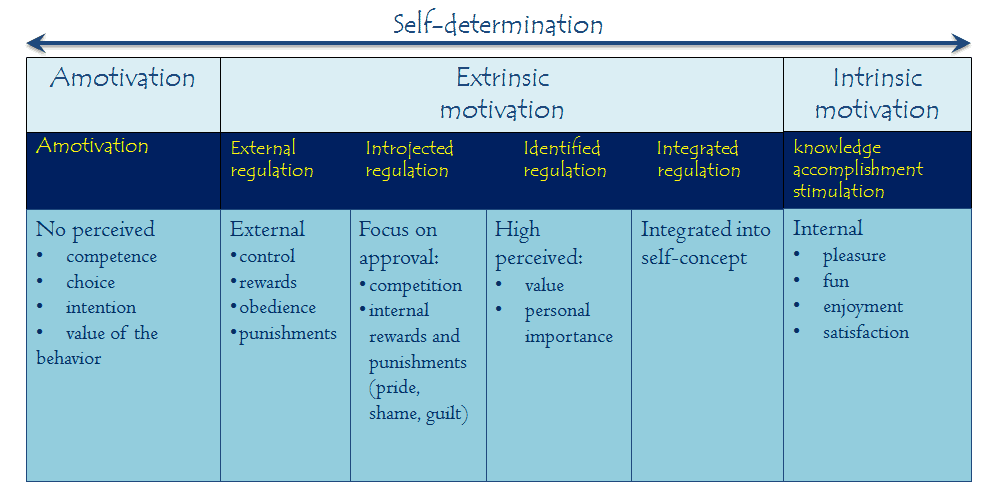
Eccles and wigfield 2002. However extrinsic motivation is argued to vary considerably in its relative autonomy and thus can either reflect external control or true self regulation. Psychology explains the difference between intrinsic and extrinsic motivation psychology explains the difference between intrinsic and extrinsic motivation. Intrinsic motivation on the other hand refers to those activities you do because you enjoy the activity itself.
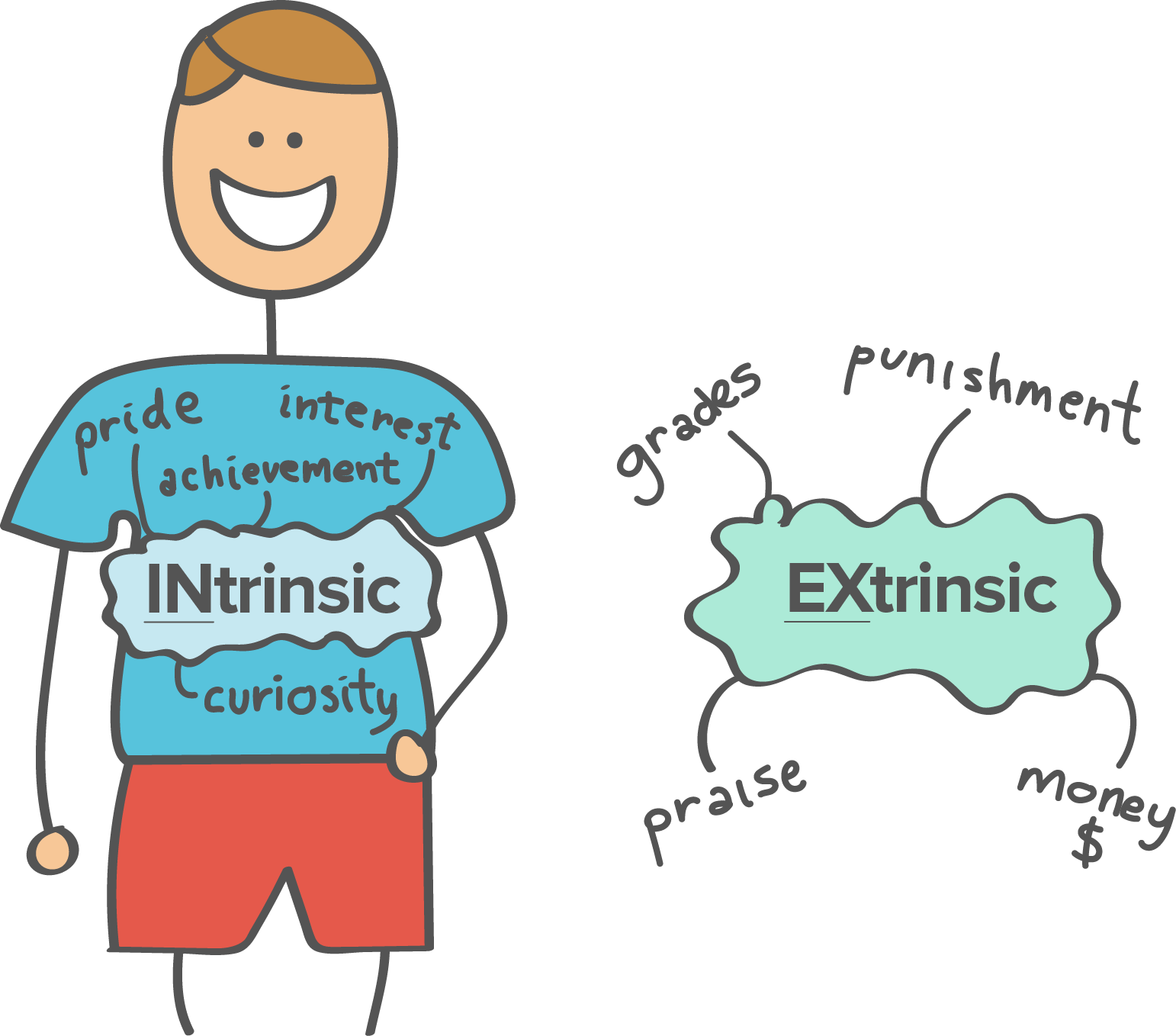
The benefit of intrinsic motivation is that it is typically a much more powerful and enduring force than extrinsic motivation. Intrinsic motivation extrinsic motivation. Intrinsic motivation vs extrinsic motivation. A genuine interest in a studied subject rather than because.
Psychology definition of intrinsic motivation. Research has shown that each type has a different effect on human behavior. Extrinsic motivation arises from outside of the individual while intrinsic motivation comes from within. Vallerand 2007 the proposed framework differentiates two main classes of benefits which determine the overall subjective expected benefit of an exercise or activity fig.
Extrinsic motivation refers to behavior that is driven by external rewards such as money fame grades and praise. Ryan and deci 2000a b. Many of the activities you engage in on a regular basic are likely driven by such internal rewards. These goals might involve work school or training for a marathon.
Building upon the distinction between intrinsic and extrinsic motivation psychological theories of motivation eg deci 1980. Studies have demonstrated that offering excessive external rewards for an already internally rewarding behavior can reduce intrinsic motivation a phenomenon known as the overjustification effect.
/2795384-differences-between-extrinsic-and-intrinsic-motivation-5ae76997c5542e0039088559.png)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/2795164-what-is-extrinsic-motivation-5b31542404d1cf0036a91c79.png)
/2795385-what-is-intrinsic-motivation-5afb187443a1030037f0b2a0.png)