Intrinsic And Extrinsic Motivation In The Classroom Pdf

Intrinsic motivation and extrinsic motivation.
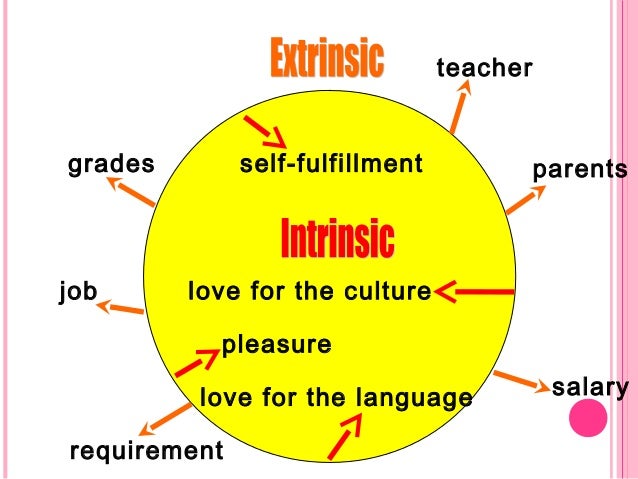
Intrinsic and extrinsic motivation in the classroom pdf. Indeed given that incentives work quite effectively in many instances one needs to understand in what cases they should be used with caution. A scale of intrinsic versus extrinsic orientation in the classroom. This post provides 18 examples of extrinsic and intrinsic motivation in the classroom. Intrinsic motivation refers to an inherent interest in pursing a topic learning for learning s sake.
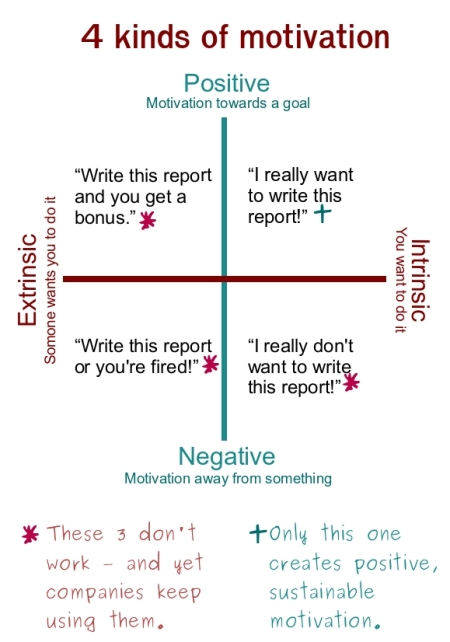
A person with extrinsic motivation wants to do a task in order to receive a reward or avoid a punishment. More generally we seek to give a precise content to the loosely defined notions of intrinsic and extrinsic motivation and. First we revisit classic definitions of intrinsic and extrinsic motivation before reviewing contemporary research on how these motivations are. Motivation is divided into two types i e.
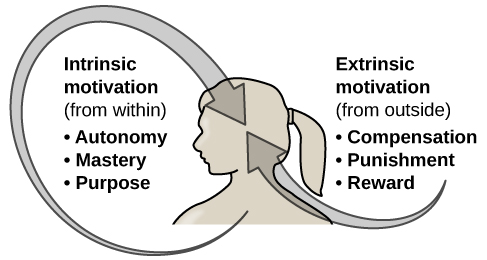
Supports in the classroom on both intrinsic and extrinsic motivational processes and students well being and academic performance. The primary motivator is internal i e. Intrinsic and extrinsic types of motivation have been widely studied and the distinction between them has shed important light on both developmental and educational practices. A person with intrinsic motivation wants to do a task for the.
You don t expect to get anything in return. You are intrinsically motivated when you do something simply because it makes you feel good is personally challenging and or leads to a sense of accomplishment. Nov 3rd 2014 by. Intrinsic and extrinsic are the two types of motivation.
Psychologists have identified two distinct forms of motivation. How to use extrinsic motivators extrinsic and intrinsic motivation operate on distinct spectrums and high rates of one do not indicate low rates of the other. In general intrinsic motivation im could be defined as an engagement in behavior that is inherently. Intrinsic and extrinsic motivation in the classroom.


/2795384-differences-between-extrinsic-and-intrinsic-motivation-5ae76997c5542e0039088559.png)